Introduction
A focal neurological deficit is a condition where a specific area of the brain, spinal cord, or peripheral nervous system is affected, leading to a loss of neurological function in a specific part of the body. Unlike generalized neurological conditions, focal deficits impact a localized area, making their diagnosis and treatment unique. This blog will explore the causes, symptoms, diagnostic methods, and treatment options for focal neurological deficits, providing a comprehensive understanding of this complex condition.
1. What is a Focal Neurological Deficit?
Definition and Overview
A loss or impairment of neurological function that is restricted to a particular area of the body is referred to as a localized neurological deficit. This condition can affect various functions, such as motor skills, sensory perception, vision, speech, or balance, depending on the affected area of the nervous system.
Common Areas Affected
Focal neurological deficits can manifest in various parts of the body, including:
- Motor Deficits: Affecting muscle strength or coordination in specific limbs.
- Sensory Deficits: Impacting sensation, such as touch, pain, or temperature.
- Cranial Nerve Deficits: Affecting vision, hearing, or facial movement.
- Cognitive Deficits: Impacting speech, language, or memory.
2. Causes of Focal Neurological Deficit
Stroke
One of the most common causes of a focal neurological deficit is a stroke. When blood flow to a specific area of the brain is interrupted, it can result in localized brain damage, leading to deficits in the area controlled by that part of the brain.
Brain Tumors
Brain tumors, whether benign or malignant, can exert pressure on surrounding brain tissue, leading to focal neurological deficits. The location of the tumor within the brain will determine the symptoms.
Traumatic Brain Injury
Head injuries can cause localized damage to the brain, resulting in focal deficits. The severity and location of the injury will determine the extent of the neurological impairment.
Infections
Infections like meningitis or encephalitis can cause inflammation in the brain or spinal cord, leading to focal deficits. These infections can damage specific areas of the nervous system, resulting in localized symptoms.
Multiple Sclerosis
An autoimmune condition known as multiple sclerosis (MS) occurs when the immune system targets the myelin sheath that surrounds nerve fibers.This can lead to focal neurological deficits, as the damage is often localized to specific areas of the brain or spinal cord.
3. Symptoms of Focal Neurological Deficit
Motor Symptoms
Motor symptoms of a focal neurological deficit may include:
- Weakness or paralysis in specific limbs.
- Loss of coordination or balance.
- An autoimmune condition known as multiple sclerosis (MS) occurs when the immune system targets the myelin sheath that surrounds nerve fibers.
Sensory Symptoms
Sensory symptoms can involve:
- Tingling or numbness in particular body parts.
- Loss of sensation in a particular limb or region.
- Changes in perception of pain or temperature.
Visual and Auditory Symptoms
- Blurred or double vision.
- Loss of vision in one eye or a specific visual field.
- Hearing loss or ringing in the ears.
Cognitive and Speech Symptoms
- Difficulty speaking or understanding language (aphasia).
- Memory loss or confusion.
- Difficulty with problem-solving or concentration.
4. Diagnosing Focal Neurological Deficit
Clinical Examination
A thorough clinical examination is the first step in diagnosing a focal neurological deficit. A neurologist will assess motor and sensory functions, reflexes, coordination, and cognitive abilities to identify the affected area.
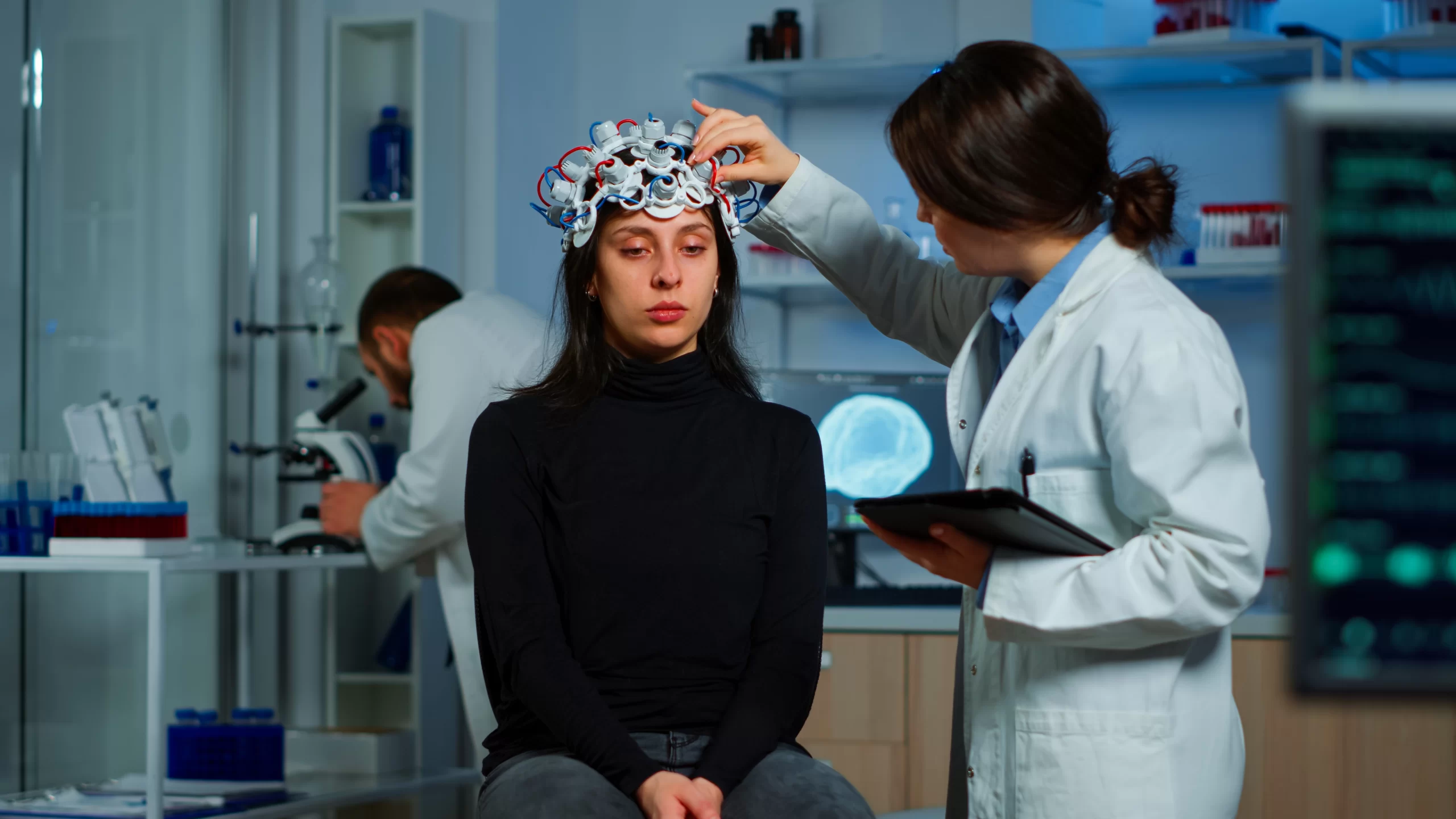
Imaging Techniques
Imaging techniques like MRI or CT scans are crucial in pinpointing the exact location and cause of the focal deficit. These scans can reveal strokes, tumors, or other abnormalities in the brain or spinal cord.
Electrophysiological Tests
Electrophysiological tests, such as an EEG or EMG, can assess the electrical activity of the brain or muscles, helping to identify the specific area of dysfunction.
Blood Tests and Lumbar Puncture
Blood tests and lumbar puncture (spinal tap) may be used to diagnose infections, autoimmune disorders, or other systemic conditions that could be causing the focal deficit.
5. Treatment Options for Focal Neurological Deficit
Medication
The treatment of a focal neurological deficit often involves medication to address the underlying cause. For example:
- Anticoagulants or thrombolytics for stroke.
- Steroids to reduce inflammation in conditions like MS.
- Antibiotics or antivirals for infections.
Surgery
In cases where a brain tumor or other structural abnormality is causing the focal deficit, surgery may be necessary to remove or reduce the mass. Neurosurgery can alleviate pressure on the affected area, potentially restoring lost function.
Rehabilitation
Rehabilitation is a key component of recovery for patients with a focal neurological deficit. Physical therapy, occupational therapy, and speech therapy can help patients regain lost functions and adapt to any permanent changes.
Lifestyle Modifications
Lifestyle modifications, such as a healthy diet, regular exercise, and avoiding smoking or excessive alcohol consumption, can help manage the risk factors associated with focal neurological deficits, particularly in cases related to stroke or cardiovascular disease.
Conclusion
A focal neurological deficit is a complex condition that requires a thorough understanding of its causes, symptoms, and treatment options. Early diagnosis and prompt treatment are essential in managing the condition and preventing further complications. If you or a loved one is experiencing symptoms of a focal neurological deficit, consulting with an expert neurologist like Dr. Nishanth at Nishanth’s Neurology Clinics can provide the specialized care needed for optimal recovery.




3 Comments
Medidove
June 20, 2019Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipisicing elit, sed do eiusmod tempor incididunt ut labore et dolore magna aliqua. Ut enim ad minim veniam, quis nostrud exercitation
Medidove
June 20, 2019Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipisicing elit, sed do eiusmod tempor incididunt ut labore et dolore magna aliqua.
Medidove
June 20, 2019Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipisicing elit, sed do eiusmod tempor incididunt ut labore et dolore magna aliqua. Ut enim ad minim veniam, quis nostrud.